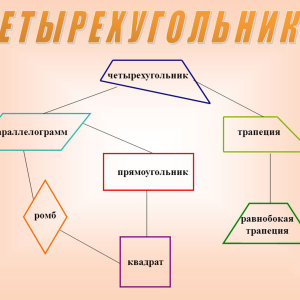
Parallelogram is a geometric figure that is often found in the tasks of the geometry course (section of the planimity). The key signs of this quadrilateral are the equality of opposite angles and the presence of two pairs of parallel opposite sides. Private cases parallelogram - rhombus, rectangle, square.
The calculation of the area of \u200b\u200bthis type of polygon can be produced in several ways. Consider each of them.
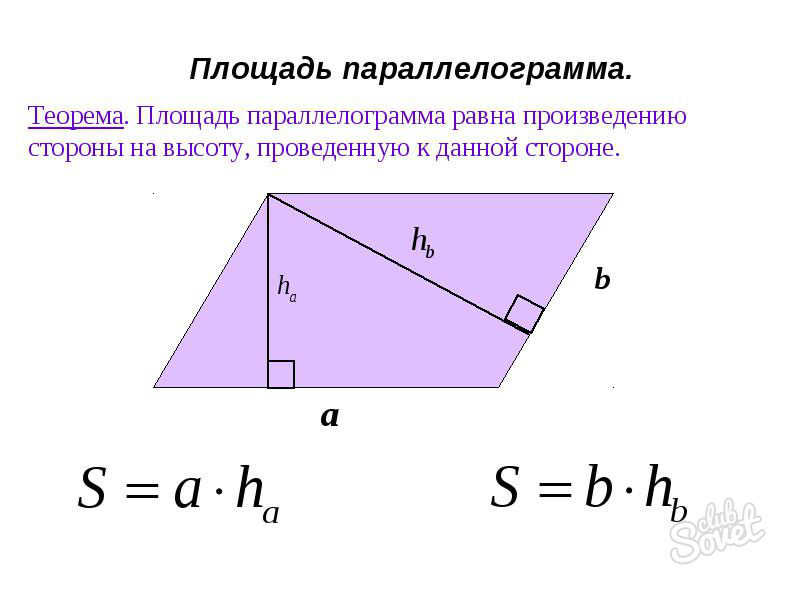
Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe parallelogram if the side and height are known
To calculate the area, the parallelogram can be used by the values \u200b\u200bof its side, as well as the length of the height, lowered to it. In this case, the obtained data will be reliable as for the case of the well-known side - the base of the figure, and if at your disposal the side side of the figure. In this case, the desired value will be obtained by the formula:
S \u003d a * h (a) \u003d b * h (b),
- S - the area that should be determined
- a, b - known (or obtained by calculations)
- h is the height, lowered to it.
Example: The value of the base of the parallelogram is 7 cm, the length of the perpendicular, lowered to it from the opposite vertex, is 3 cm.
Solution: S \u003d A * H (a) \u003d 7 * 3 \u003d 21.
Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe parallelogram if 2 sides and angle between them are known
Consider the case when you know the magnitude of the two sides of the figure, as well as a degree of the angle, which they form among themselves. The data provided can also be used to find the parallelogram area. In this case, the formula expression will have the following form:
S \u003d a * c * sinα \u003d a * c * sinβ,
- S is an area that should be determined
- a - side,
- c - known (or obtained by calculations) base,
- α, β - angles between the parties a and c.
Example: The base of the parallelogram is 10 cm, its lateral side is 4 cm less. A stupid angle of the figure is 135 °.
Solution: Determine the value of the second side: 10 - 4 \u003d 6 cm.
S \u003d A * C * sinα \u003d 10 * 6 * sin135 ° \u003d 60 * sin (90 ° + 45 °) \u003d 60 * cos45 ° \u003d 60 * √2 / 2 \u003d 30√2.
Find a parallelogram area if diagonals and angle are known between them
The presence of known values \u200b\u200bof diagonals of this polygon, as well as the angle that they form as a result of their intersection, allows you to determine the size of the figure of the figure.
S \u003d (d1 * d2) / 2 * sinγ
S \u003d (d1 * d2) / 2 * sinφ,
S is an area that should be determined
D1, D2 - known (or obtained by calculations) diagonal,
γ, φ - angles between diagonals D1 and D2.
In addition, you should not forget that the area of \u200b\u200bthe whole figure consists of the areas of all its parts.